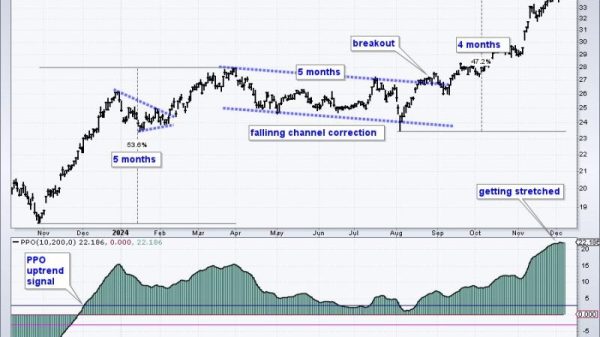
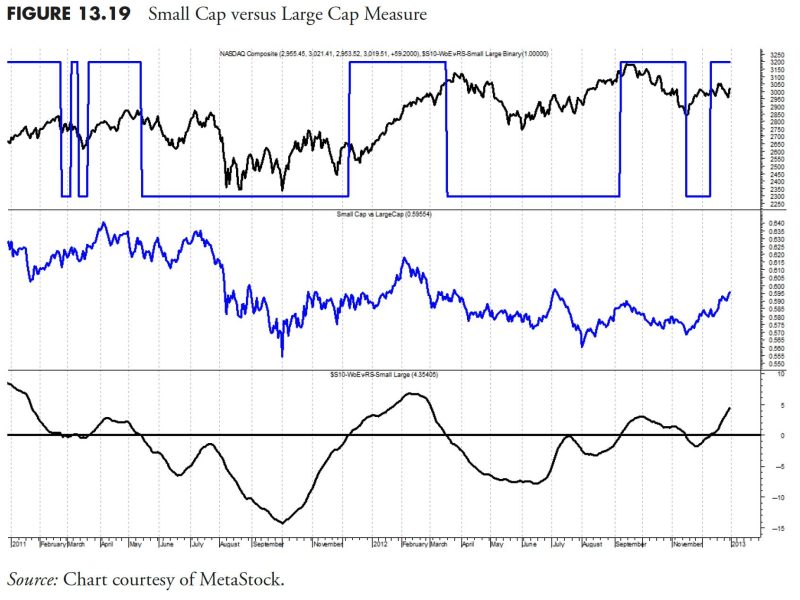
In the realm of financial management and investing, there exist numerous methodologies and strategies aimed at maximizing returns and minimizing risks. One such approach that garners attention is rules-based money management. This strategy is grounded in the principle of using pre-determined guidelines and criteria for making investment decisions rather than relying solely on emotions or predictions. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of rules-based money management, particularly focusing on the concept of relative strength and other key measures that play a pivotal role in this method.
Relative strength is a fundamental concept within rules-based money management that involves comparing the performance of an asset or security against a benchmark or other investments. By scrutinizing the relative strength of various assets, investors can identify those that are exhibiting strong momentum and potentially outperforming the broader market. This information serves as a valuable input for investment decisions, helping investors tilt their portfolios towards assets with robust relative strength while avoiding underperforming assets.
One of the key advantages of using relative strength in rules-based money management is its ability to provide a systematic and objective measure of asset performance. Rather than relying on subjective assessments or predictions, investors can leverage concrete data and metrics to evaluate the strength of different investments. This data-driven approach not only enhances the transparency and consistency of investment decisions but also helps in reducing the impact of biases and cognitive errors that often plague human decision-making.
In addition to relative strength, several other measures and indicators are integral to the framework of rules-based money management. For instance, technical analysis tools such as moving averages, trend lines, and momentum indicators play a crucial role in identifying market trends and potential entry or exit points. By incorporating these tools into their analysis, investors can gain insights into the underlying dynamics of the market and make more informed decisions based on objective criteria rather than gut feelings.
Risk management is another cornerstone of rules-based money management, emphasizing the importance of preserving capital and mitigating downside risk. Through the use of stop-loss orders, position sizing techniques, and portfolio diversification, investors can safeguard their investments against adverse market movements and limit potential losses. By adhering to strict risk management rules, investors can maintain discipline and consistency in their approach, which is essential for long-term success in the financial markets.
Overall, rules-based money management offers a structured and systematic framework for making investment decisions based on objective criteria and measures. By incorporating concepts like relative strength, technical analysis, and risk management into their strategy, investors can enhance their chances of achieving consistent returns and weathering market volatility effectively. While no approach is foolproof, adopting a rules-based methodology can provide greater clarity, discipline, and resilience in navigating the complexities of the financial markets.