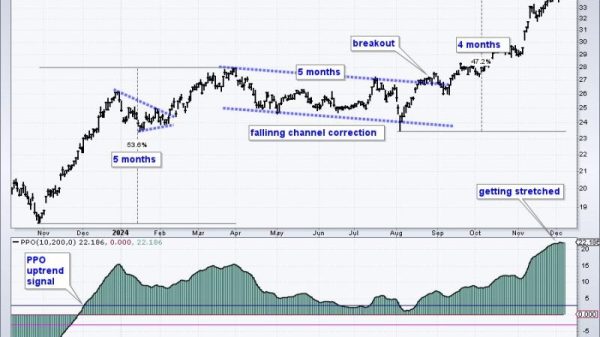
Sector rotation in the stock market is a concept that can provide valuable insights into where investors are putting their money. By analyzing how capital flows between different sectors, traders can gain a better understanding of the overall market sentiment and potential future trends. However, interpreting these signals can sometimes lead to conflicting stories.
One of the primary reasons for conflicting narratives in sector rotation is the diverse range of factors influencing investor decisions. Market participants have varying strategies, risk tolerances, and goals, which can lead to divergent moves in the market. For instance, a growth-oriented investor might favor technology and consumer discretionary stocks, while a more defensive investor could be inclined towards utilities and healthcare.
Another factor contributing to conflicting stories in sector rotation is market volatility and external events. Sudden shifts in economic data, geopolitical tensions, or natural disasters can disrupt sector performance and create anomalies in the rotation pattern. Additionally, unexpected news or policy announcements can trigger sharp movements in certain sectors, influencing the overall narrative.
Moreover, the timeframe and methodology used to analyze sector rotation can also result in conflicting interpretations. Short-term traders focusing on daily or weekly movements may see different sector leadership compared to long-term investors looking at monthly or quarterly trends. Different analytical models, such as relative strength, momentum, or fundamental analysis, can lead to diverse conclusions about sector rotation dynamics.
Furthermore, investor sentiment and market psychology play a significant role in shaping conflicting stories in sector rotation. Emotions like fear, greed, and herd behavior can drive capital into certain sectors while discarding others, creating temporary imbalances in the market. These sentiments can shift rapidly, causing conflicting narratives to emerge as investors reassess their positions.
Another crucial aspect that can contribute to conflicting stories in sector rotation is the composition of benchmark indices. Different index providers have varying sector weightings and methodologies, leading to discrepancies in sector performance and rotation signals. Investors tracking different benchmarks may observe conflicting stories in sector dynamics, creating confusion in interpreting market trends.
In conclusion, sector rotation is a valuable tool for understanding market dynamics and investor behavior. However, conflicting stories can arise due to the diversity of factors influencing sector performance, market volatility, analysis timeframe, investor sentiment, and index composition. To navigate these conflicting narratives effectively, investors should consider a holistic approach that combines multiple perspectives and strategies to gain a comprehensive view of sector rotation trends.