Sector rotation is a crucial strategy employed by top investors to navigate market fluctuations and capitalize on emerging opportunities. By carefully monitoring market trends and economic indicators, seasoned investors can effectively reallocate their assets to sectors poised for growth. Here are three key ways that top investors track sector rotation to inform their investment decisions:
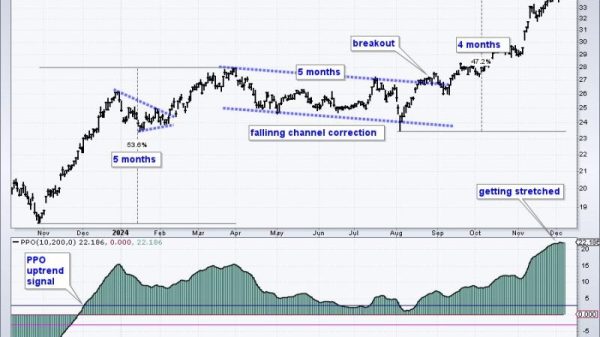
1. **Technical Analysis:** Top investors often rely on technical analysis to identify sector rotation trends. This involves analyzing historical price data and market patterns to predict future price movements. By studying charts and using tools like moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Fibonacci retracements, investors can detect shifts in sector momentum. For example, if a sector consistently outperforms the broader market or shows signs of bullish price action, it may indicate a rotation towards that sector. Conversely, a sector experiencing weakening price trends might signal a rotation away from it. By staying abreast of technical developments, investors can position themselves ahead of sector rotations and capitalize on market opportunities.
2. **Fundamental Analysis:** Fundamental analysis is another essential tool utilized by top investors to track sector rotation. By delving into the financial health and performance of companies within different sectors, investors can gauge industry trends and forecast future prospects. Key metrics such as revenue growth, earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, and debt levels offer valuable insights into sector dynamics. For instance, if a sector shows strong fundamentals like robust earnings growth, solid balance sheets, and favorable industry outlooks, it may attract investor interest and undergo rotation. Conversely, sectors with deteriorating fundamentals or facing external challenges may experience rotations away from them. By conducting thorough fundamental analysis, investors can identify sector rotation opportunities and adjust their portfolios accordingly.
3. **Macroeconomic Indicators:** Tracking macroeconomic indicators is another vital strategy employed by top investors to monitor sector rotation. Economic data such as GDP growth, inflation rates, interest rates, and employment figures can provide valuable insights into sector performance. For example, sectors like technology and healthcare may benefit from strong economic growth and consumer spending, while defensive sectors like utilities and consumer staples may outperform during periods of economic uncertainty. By staying informed about macroeconomic trends and policy developments, investors can anticipate sector rotations driven by broader economic conditions. For instance, rising interest rates may prompt a shift towards financials and cyclical sectors, while falling commodity prices could impact energy and materials sectors. By aligning their investment decisions with macroeconomic indicators, top investors can navigate sector rotations effectively and optimize their portfolio returns.
In conclusion, tracking sector rotation is a critical strategy for top investors seeking to maximize their investment returns and adapt to changing market conditions. By leveraging technical analysis, fundamental research, and macroeconomic insights, investors can identify sector trends, anticipate rotations, and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Through a disciplined and proactive approach to sector rotation, investors can enhance portfolio performance, mitigate risks, and achieve their long-term investment objectives.