Stock Market Rally and Yield Rise: Factors and Implications
Factors Driving the Stock Market Rally:
1. Economic Reopening: The gradual reopening of economies post-pandemic is a key factor driving the stock market rally. Businesses are resuming operations, leading to increased consumer spending and improving corporate earnings. This optimism has boosted investor confidence, resulting in a surge in stock prices.
2. Government Stimulus: To mitigate the economic impact of the pandemic, governments worldwide have implemented massive stimulus packages. These measures include direct payments to individuals, loans to businesses, and infrastructure spending. The injection of liquidity into the financial system has provided support to stock markets.
3. Low Interest Rates: Central banks have maintained historically low interest rates to stimulate economic growth. Low rates make equities more attractive compared to bonds and other fixed-income securities. Investors seeking higher returns have turned to the stock market, driving up stock prices.
4. Technology and Innovation: The accelerated adoption of technology and innovation during the pandemic has fueled the performance of tech stocks and other growth sectors. Companies at the forefront of digital transformation have outperformed traditional businesses, contributing to the stock market rally.
Yield Rise and Its Implications:
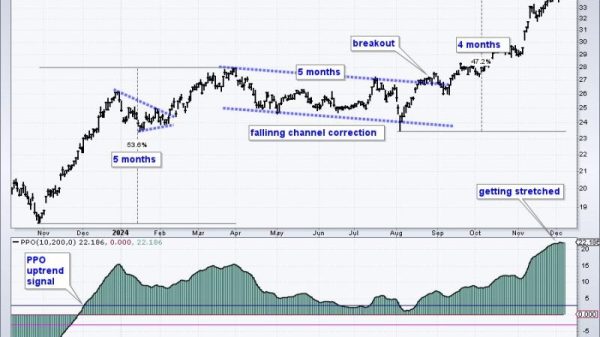
1. Bond Market Volatility: The increase in yields on government bonds, particularly the 10-year Treasury yield, has led to volatility in the bond market. Rising yields make existing bonds less attractive, causing bond prices to fall. Investors have shifted their focus from bonds to stocks in search of better returns.
2. Rotation in Equity Markets: The rise in yields has prompted a rotation in equity markets, with investors favoring value stocks over growth stocks. Value stocks, often characterized by stable revenues and dividends, are perceived as less sensitive to interest rate changes. This shift has created opportunities for investors to diversify their portfolios.
3. Impact on Mortgage Rates: The uptick in bond yields has translated into higher mortgage rates, affecting the housing market. Higher rates could dampen demand for homes and lead to a slowdown in the housing sector. Prospective homebuyers may face increased borrowing costs, impacting affordability.
4. Inflation Concerns: The increase in yields has raised concerns about inflationary pressures. Higher inflation erodes purchasing power and can lead to higher interest rates in the future. Investors are closely monitoring inflation indicators to assess the Federal Reserve’s response and potential policy adjustments.
In conclusion, the stock market rally and yield rise reflect the complex interplay of economic factors and investor sentiment. Understanding the driving forces behind these trends is essential for investors to make informed decisions and navigate the evolving financial landscape. As markets continue to adapt to changing conditions, staying informed and adapting investment strategies will be crucial for long-term success.