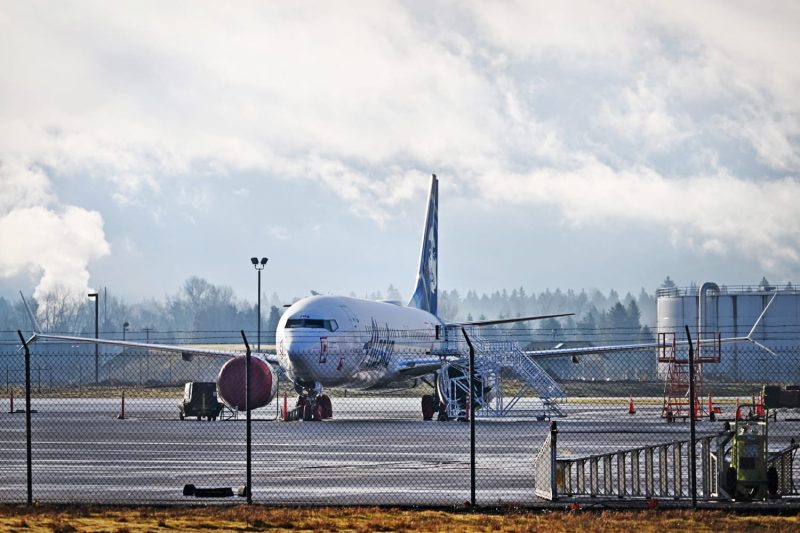
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has recently taken significant steps to enhance its oversight of Boeing 737 Max 9 jets following a near-disaster involving an Alaska Airlines flight. The incident highlighted critical concerns about the safety and regulatory compliance of these aircraft, leading to the implementation of new measures to ensure passenger safety.
The incident in question occurred when an Alaska Airlines flight experienced issues with its autopilot system, causing the plane to suddenly pitch downward. The flight crew was able to regain control, averting a potential catastrophe. However, the incident raised alarming questions about the safety protocols and regulatory oversight of Boeing 737 Max 9 jets.
As a result, the FAA has stepped up its efforts to address these concerns. One key area of focus is the review of Boeing’s automated flight control system, known as the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS). This system played a critical role in the two fatal crashes involving Boeing 737 Max planes in 2018 and 2019, leading to the worldwide grounding of these aircraft.
The FAA has now committed to providing additional oversight and scrutiny of the MCAS system. This includes a comprehensive review of its design and functionality, ensuring that it meets stringent safety standards and is not susceptible to potential malfunctions. The agency has also vowed to improve the communication and collaboration between Boeing and FAA engineers, fostering a more thorough understanding of the MCAS system’s operations.
Additionally, the FAA plans to enhance pilot training requirements for Boeing 737 Max 9 jets. The agency will work closely with airlines and pilot unions to develop new training programs that emphasize the specific characteristics and potential challenges associated with these aircraft. This will include extensive simulator-based training and mandatory recurrent training for pilots already qualified to fly the Boeing 737 Max 9.
The increased oversight by the FAA also involves enhanced regulatory inspections and audits. Inspectors will conduct more frequent and in-depth examinations of maintenance practices, records, and operational procedures related to Boeing 737 Max 9 aircraft. This proactive approach aims to ensure that all airlines operating these jets are in full compliance with safety regulations and that any potential issues are identified and rectified promptly.
Moreover, the FAA has established a robust reporting and feedback mechanism to encourage pilots, technicians, and other aviation professionals to raise safety concerns without fear of reprisal. This confidential reporting system will enable the FAA to gather vital information about potential problems or risks, allowing for prompt action and the implementation of necessary measures to prevent accidents.
The recent near-disaster involving an Alaska Airlines flight has served as a wake-up call for the FAA and the aviation industry as a whole. It has highlighted the importance of continuous improvement and the need for comprehensive oversight to ensure passenger safety. The measures implemented by the FAA in response to this incident demonstrate a commitment to learning from past mistakes and preventing future accidents.
With the increased scrutiny of the MCAS system, enhanced pilot training requirements, more rigorous inspections, and the establishment of a confidential reporting system, the FAA aims to restore public trust in the safety of Boeing 737 Max 9 jets. By ensuring that these aircraft meet the highest standards of safety and regulatory compliance, the FAA is taking significant steps towards preventing future incidents and safeguarding the lives of passengers and crew members.