– Moving Beyond the 7% Barrier: The Impact of Stronger Economic Data on Mortgage Rates –
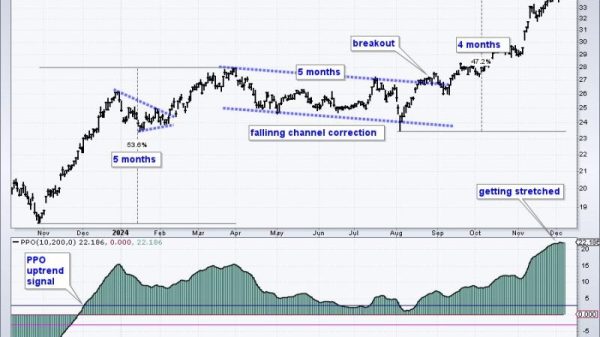
Economic data plays a significant role in shaping the mortgage market. As the global economy recovers from the turmoil caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, signs of stronger economic performance are beginning to emerge. This newfound stability has led to a rise in mortgage rates, with some surpassing the 7% mark for the first time in years. In this article, we will explore the factors behind this upward trend and the potential implications for homeowners and prospective buyers.
It is no secret that the pandemic wreaked havoc on economies worldwide. Governments, central banks, and financial institutions responded with various measures to stabilize the situation. From a mortgage perspective, this led to historically low interest rates. However, as economies gain momentum, and signs of recovery become more evident, investors are becoming increasingly confident. This newfound optimism is driving mortgage rates higher.
One key factor influencing the surge in mortgage rates is inflation. With economic growth gaining traction, the demand for goods and services has increased. The consequential rise in demand is putting upward pressure on prices, leading to inflationary concerns. In response, central banks may choose to increase interest rates to curb inflation, which invariably affects mortgage rates.
Another critical aspect contributing to the uptick in mortgage rates is the increased risk appetite among investors. As economies recover and businesses flourish, investors are looking for new investment opportunities. This shift in preferences drives funds away from safer assets, such as government bonds, towards riskier investments, such as stocks. Consequently, this reduced demand for bonds leads to higher bond yields and an increase in mortgage rates since they are closely tied to bond yields.
The rise in mortgage rates brings forth implications for both existing homeowners and prospective buyers. Existing homeowners, especially those with adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), may experience higher monthly payments as rates reset. It is prudent for homeowners with ARMs to assess their financial situation and consider refinancing into a fixed-rate mortgage to lock in lower rates before they rise further.
For prospective homebuyers, higher mortgage rates mean reduced affordability. As rates surpass the 7% threshold, the overall cost of borrowing increases significantly. This increase in borrowing costs may discourage some buyers from entering the market or force them to downsize their purchasing power. It becomes crucial for potential buyers to carefully evaluate their financial standing, taking into account the impact of higher rates on their mortgage payments.
Despite the challenges posed by rising mortgage rates, it is essential to recognize them as a reflection of a recovering economy. While homeowners will face higher costs, it also signifies increased economic activity and growth potential. It is crucial for borrowers to remain vigilant, take advantage of available resources, and seek advice from mortgage professionals.
In conclusion, as the economy rebounds from the effects of the pandemic, stronger economic data is fueling a rise in mortgage rates. Factors such as inflation, increased risk appetite among investors, and shifts in global financial markets contribute to this upward trend. Existing homeowners with adjustable-rate mortgages should consider taking advantage of lower rates by refinancing into fixed-rate mortgages. Potential buyers need to evaluate their financial capabilities against higher borrowing costs. Ultimately, understanding the impact of strong economic data on mortgage rates is vital in making informed decisions about homeownership and financing.