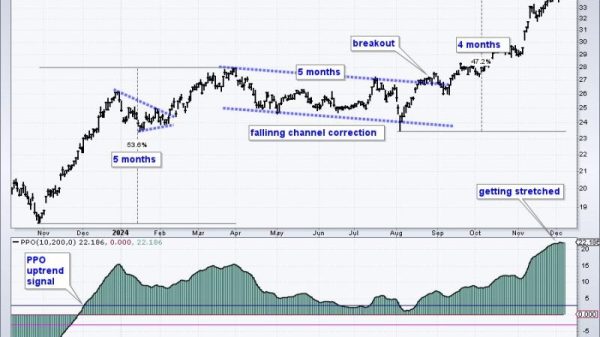
The article titled Inflation Rate Falls to 2.9% in July, Adding to Signs That Surging Prices Have Abated provides insight into the recent decline in the inflation rate in July. Inflation is a crucial economic indicator that measures the rate at which prices for goods and services rise, leading to a decrease in purchasing power for consumers. The inflation rate falling to 2.9% in July suggests that the pace of price increases has slowed, offering some relief amid concerns of surging inflationary pressures in recent months.
One of the key factors contributing to the decline in the inflation rate is the stabilization of global commodity prices. Commodity prices play a significant role in driving inflation, particularly in sectors such as energy, food, and raw materials. The gradual easing of supply chain disruptions and production constraints has helped alleviate some of the price pressures seen earlier in the year, leading to a moderation in overall inflation levels.
Additionally, the article highlights that the central bank’s monetary policy measures have also played a role in tempering inflationary expectations. Central banks often use interest rate adjustments and other monetary tools to influence inflation trends. In response to the potential threat of runaway inflation, central banks may choose to tighten monetary policy, which can help cool down the economy and prevent excessive price increases.
Moreover, the article mentions the importance of consumer spending patterns in shaping inflation dynamics. Consumer demand is a crucial driver of inflation, as higher levels of spending can push up prices. The recent moderation in inflation could be reflective of changes in consumer behavior, with individuals and households adjusting their consumption patterns in response to changing economic conditions.
Furthermore, the article emphasizes the role of government policies in managing inflation. Fiscal policies, such as taxation and government spending, can impact inflation by influencing aggregate demand in the economy. By implementing appropriate fiscal measures, governments can help stabilize prices and prevent excessive inflationary pressures.
In conclusion, the recent decline in the inflation rate to 2.9% in July provides a positive signal that surging prices may have abated. Factors such as stabilization in commodity prices, central bank interventions, consumer spending patterns, and government policies have all played a part in influencing inflation trends. Monitoring inflation dynamics and implementing appropriate policy responses will be crucial in maintaining price stability and supporting economic growth in the future.