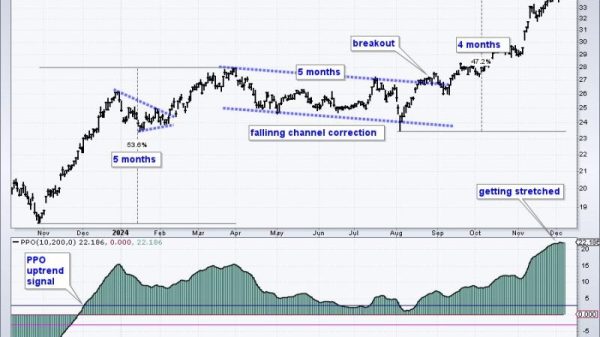
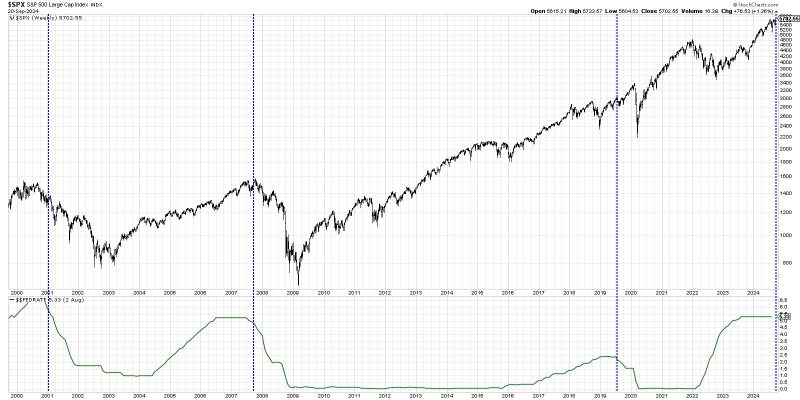
As the global economy faces uncertainties and challenges, central banks have been implementing various monetary policies to stimulate economic growth and stabilize financial markets. One of the key tools at their disposal is the adjustment of interest rates, commonly referred to as rate cuts. However, the impact of rate cuts on stock performance is a topic of ongoing debate among investors and analysts.
Proponents of rate cuts argue that reducing interest rates can boost economic activity by making borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers. Lowering borrowing costs can encourage investment and consumption, driving corporate earnings and ultimately leading to higher stock prices. In times of economic downturn or market instability, rate cuts are seen as a powerful tool to support financial markets and restore investor confidence.
On the other hand, critics of rate cuts warn of potential negative consequences for stock performance. They argue that prolonged periods of low interest rates can distort market valuations, leading to asset bubbles and excessive risk-taking by investors. Moreover, ultra-low rates can erode the profitability of financial institutions, especially banks, which rely on the spread between borrowing and lending rates for income. In such scenarios, stock prices may become disconnected from underlying fundamentals, creating a volatile and unpredictable market environment.
Historical data provides mixed evidence on the relationship between rate cuts and stock performance. Some studies suggest that equity markets tend to rally in the immediate aftermath of rate cuts, as investors anticipate lower borrowing costs and increased economic activity. However, the long-term impact of rate cuts on stock returns is less clear, with market reactions influenced by a host of other factors such as corporate earnings, geopolitical developments, and macroeconomic trends.
Investors should exercise caution when interpreting the effects of rate cuts on stock performance and consider the broader economic context in their decision-making. While interest rate policy can shape market sentiment and investor behavior, it is just one of many factors influencing stock prices. Sound investment strategies should be grounded in thorough research, diversification, and a long-term perspective that looks beyond short-term fluctuations driven by monetary policy decisions.
In conclusion, the debate over the impact of rate cuts on stock performance is complex and multifaceted, reflecting the nuanced interplay between monetary policy, market dynamics, and investor sentiment. While rate cuts can provide temporary relief to financial markets and stimulate economic activity, their long-term consequences for stock prices remain uncertain. Investors should maintain a disciplined and informed approach to navigating changing market conditions, recognizing that rate cuts are just one piece of the puzzle in the broader landscape of investment strategies and risk management.