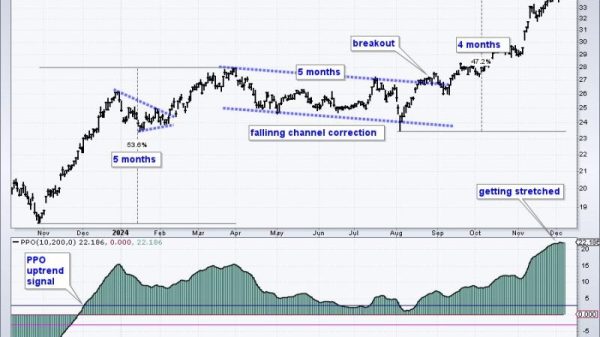
The Treasury Long-Term (TLT) ETF has been facing downwards pressure in recent days, causing concern among investors in the fixed-income market. As TLT continues its downtrend, it is anticipated that interest rates will rise, impacting various sectors of the economy and financial markets. Let’s delve into the potential effects of this trend on different aspects of the economy.
1. **Housing Market**: One of the sectors that could be significantly impacted by rising interest rates is the housing market. As interest rates increase, borrowing costs for mortgages will also go up. This can lead to a decrease in demand for housing as potential homebuyers may find it more expensive to finance their purchases. Consequently, this could slow down the pace of home sales and potentially even affect property values.
2. **Corporate Investments**: Rising interest rates can also have repercussions on corporate investments. Companies that heavily rely on borrowing to fund their operations or expansions may face higher costs as borrowing becomes more expensive. This can lead to a decrease in capital expenditures and potentially impact the overall growth and profitability of businesses across various industries.
3. **Fixed-Income Investments**: Investors holding fixed-income securities, such as bonds, may see a decline in the value of their investments as interest rates rise. When interest rates go up, new bonds issued in the market offer higher yields, making existing bonds with lower yields less attractive. This can lead to a decrease in the market value of existing bonds, impacting investors holding these securities in their portfolios.
4. **Equity Markets**: The relationship between interest rates and equity markets is complex and can vary based on different factors. In general, rising interest rates can lead to higher borrowing costs for companies, which may affect their earnings and, in turn, stock prices. However, other factors such as economic growth, inflation expectations, and monetary policy can also influence equity markets, making it challenging to predict the overall impact of rising interest rates on stock prices.
5. **Consumer Spending**: Higher interest rates can also influence consumer spending patterns. As borrowing costs increase, consumers may cut back on discretionary spending, such as durable goods purchases and leisure activities. This can have a ripple effect on the overall economy, as consumer spending is a significant driver of economic growth.
In conclusion, the resumption of the downtrend in TLT and the expected rise in interest rates can have far-reaching implications for various sectors of the economy. Investors and market participants should closely monitor these developments and adjust their strategies accordingly to navigate the changing landscape of the financial markets.